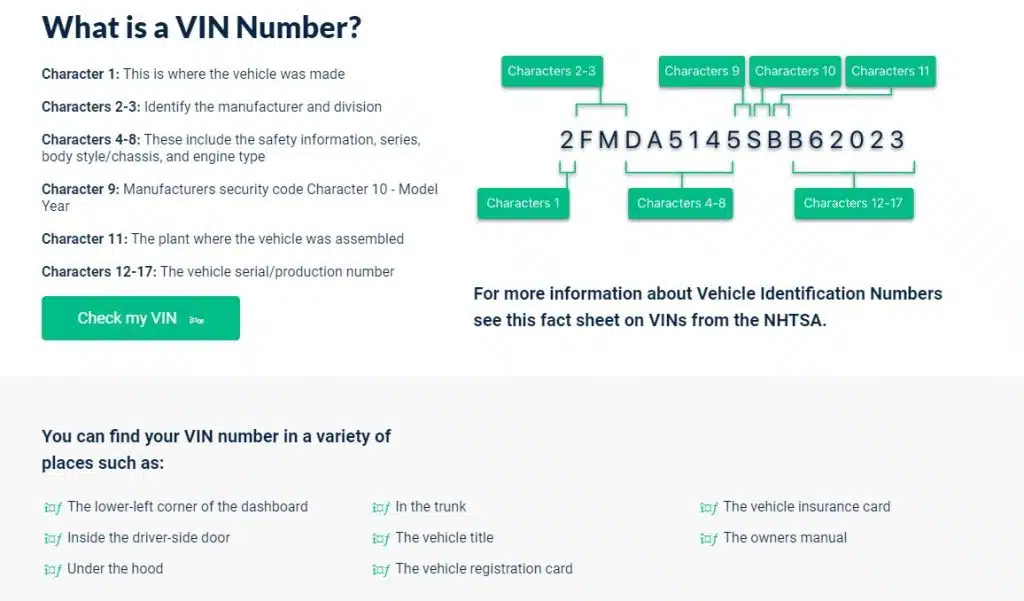
If you are considering an electric vehicle, one of the first things you will need to learn is about charging. Electric vehicles will charge differently and have different distances that they can travel based on the type of charging you use.
The Three Types of Power For Electric Car Charging
Standard Charging
Standard charging is the term used for when you come home and plug your vehicle into a regular 120v outlet in your home. This is a very common way to charge a vehicle and for charging electric cars.
Standard charging is very slow because it is using the lowest volts possible to charge the vehicle. Depending on the age of your vehicle, a charge can take between 10 and 12 hours for a full battery charge. When you charge electric car with a low volt charge, you should be able to add about 5 miles per hour charged to your battery for about 60 miles for a 12-hour charge.
The drawback to running your vehicle on standard charging is that it takes 12 hours to get a charge, and you are only gaining about 5 miles per hour. If you arrive home late one evening, forget to charge your vehicle until right before bed, or have a long drive the next day, this could present a problem. There are many factors that affect the charging of an electric vehicle. Charging time and charge speeds when charging an electric car, including the type of power source can impact the hours to charge your EV.
Faster Charging / 240 V Charging
Most charge stations are equipped with 240-volt chargers as a power source for faster charging and to charge electric vehicles. Many people also opt to have this type of charging station installed in their personal garage for convenience. A 240v charge is a better charging option, especially for newer vehicles.
When you use a 240-volt charger, like the Tesla model, you are adding about 25 miles per hour charged to your vehicle. For an overnight charge of 10 hours, that is 250 miles. This is great for when you are traveling or when you will not have access to a charger for a day or two while your vehicle charges.
Since most people do not want to leave their vehicles at a gas station charging for 10 hours, they often do charge-ups throughout the day, such as when they stop for lunch or when they have a meeting. This is one of the reasons that many people have a 240-volt system installed at home.
However, it is important to remember that the type of battery system you have in your vehicle can impact how many miles are available when charging. Even on a 240-volt charger, some systems will only acquire about 13-15 miles of charge per hour.
Super Charging
Super charging electric cars or fast charging is available at some charging stations. This type of charging will usually only work with newer vehicles. It is important to check your vehicle to see if it can handle a fast charge before connecting your vehicle to the system.
These systems can bring your car up to about 80 percent charged in about an hour from being almost empty. This translates to about 200 miles per charge hour for electric vehicles charge.
Tesla has super charging stations that will provide an even faster charge, but these are designed to only accommodate some Tesla models. All Teslas, however, can accommodate generic super charging stations.
The one drawback to this is the price. Since you literally “fill” your battery in less than an hour, these charging stations often cost more than your 240-volt stations. In fact, you can expect to pay about the same amount as you would a tank versus f gas Electric Car Charging
Unless it was specifically designed for fast charging, fast charging your battery places a lot of wear and tear on your battery. S steady charge like you get from your home or from a 240-volt charge is better for the life of your battery.
Finding fast charging stations is a little more difficult, especially if you do not have a Tesla. There are approximately 40,000 charging stations nationwide for public use for electric vehicles. Of those stations, only 5,000 are super chargers. Even the Tesla model fast charging stations are spread out sparsely and are not as readily available as their regular charging stations for vehicle charges.

The Future Of Electric Car Charging
As more electric vehicles enter the market and technology improves, charging will continue to change. You can anticipate that more charging stations will become available as the demand for these vehicles continues to increase.
Many public parking lots are now including charging stations, and nearly all new construction includes a few spaces where cars can charge.
A Note On Charging Distances
It is also important to remember that how far your vehicle will travel on each charge will depend on how you drive your vehicle. Hard stops and quick accelerations use more electricity and deplete the mileage.
Long runs down the highway will use more electricity than stop-and-go traffic, and the amount you use your air conditioner or heater can also impact the number of miles you will get between charging. Electric vehicles also use more electricity when operating in colder climates than in warmer ones, which can also reduce mileage.
When Purchasing A Vehicle
Always remember to have a VINsmart report run on the vehicle before making any vehicle purchase. A VINsmart report runs a complete history on the vehicle including whether it has ever been reported as stolen, has been involved in a major accident, or has been listed as a totaled vehicle.
VINsmart reports will also give you a history of every time the vehicle has been registered as well as a history of the mileage. It reports any significant incidents related to the vehicle, such as being involved in a fire or flood.
When you are going to purchase a used vehicle, the best way to ensure you are making a good purchase is to know the vehicle’s complete history.